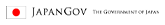Integrated Air and Missile Defense
Missile defense operation and ongoing efforts
“Ballistic missiles” refer to missiles that fly following a ballistic trajectory that is a parabolic path after being launched by a rocket engine
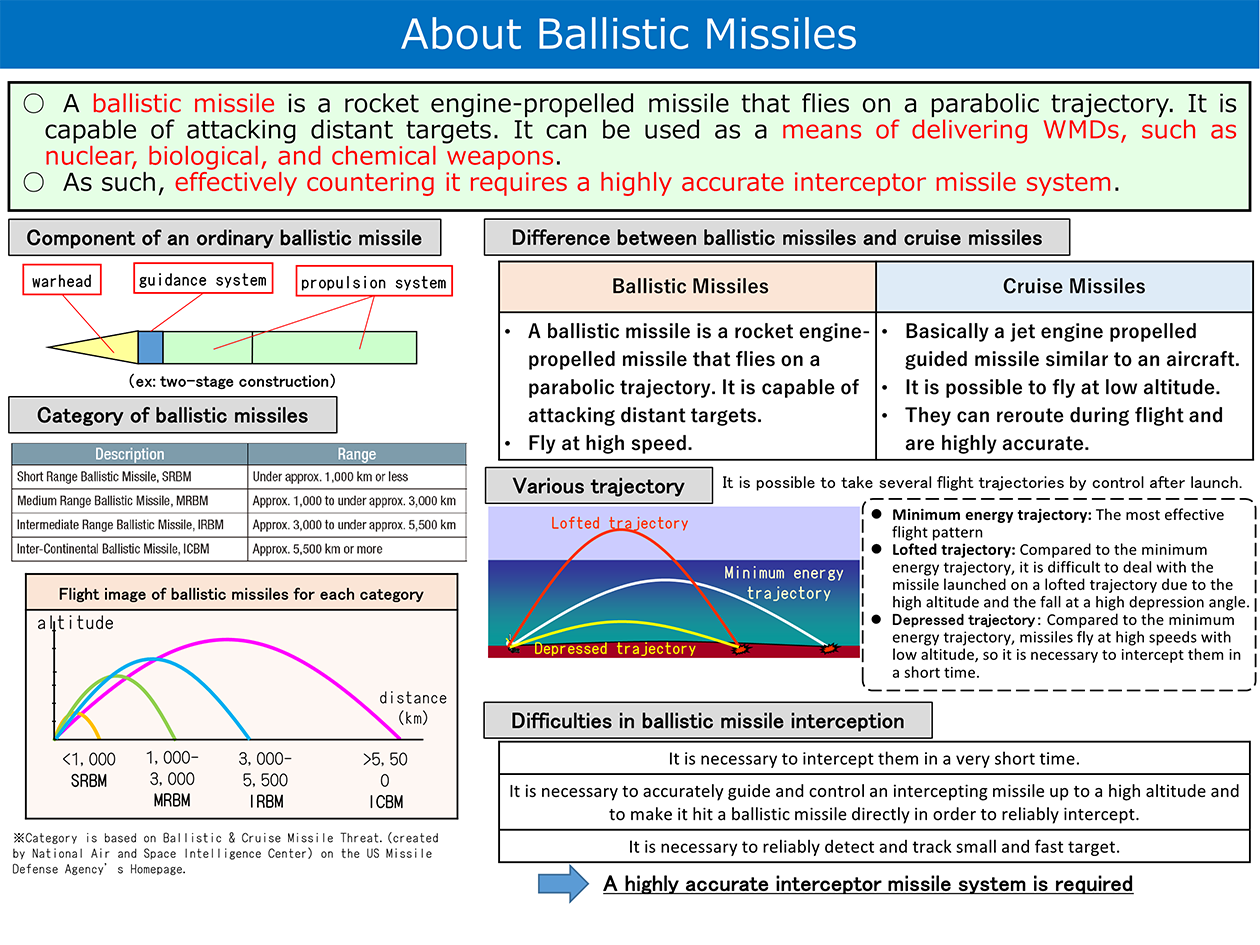
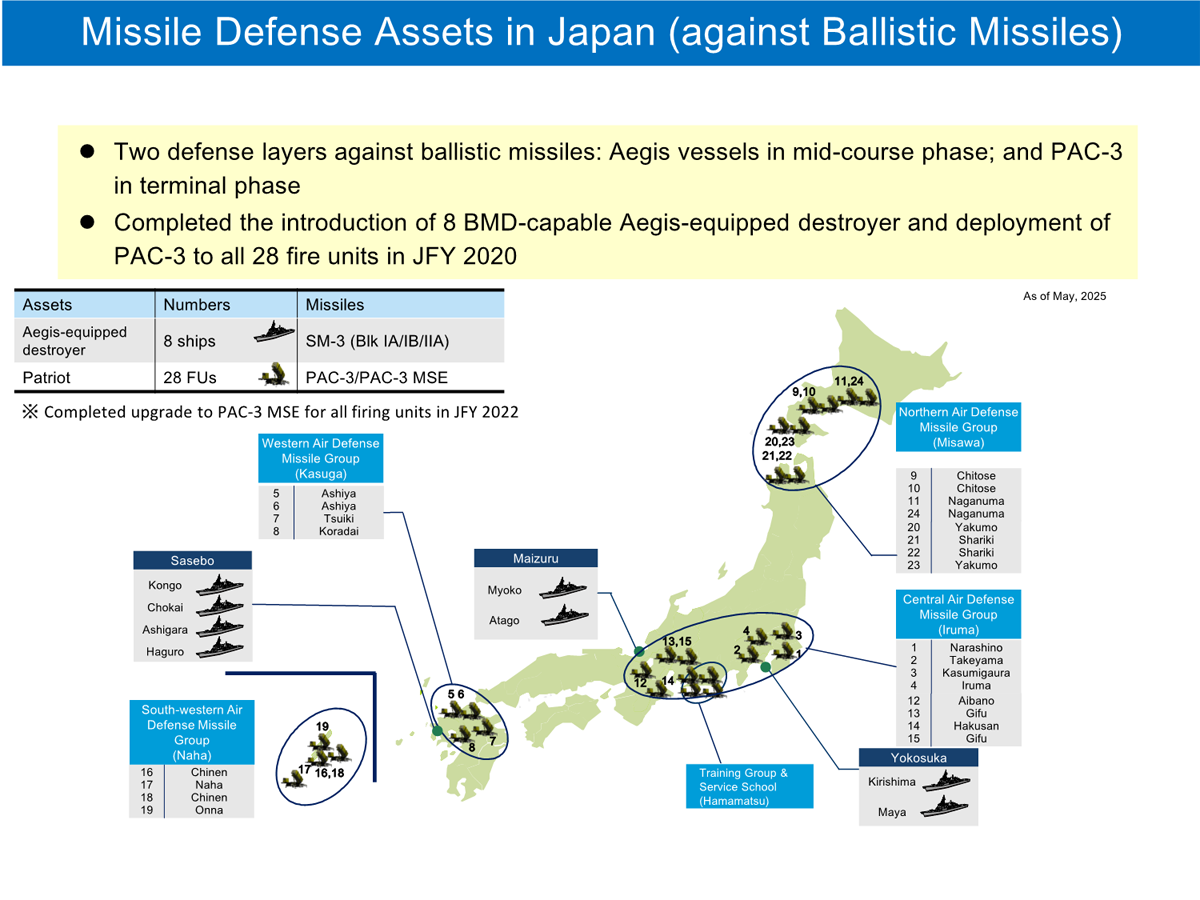
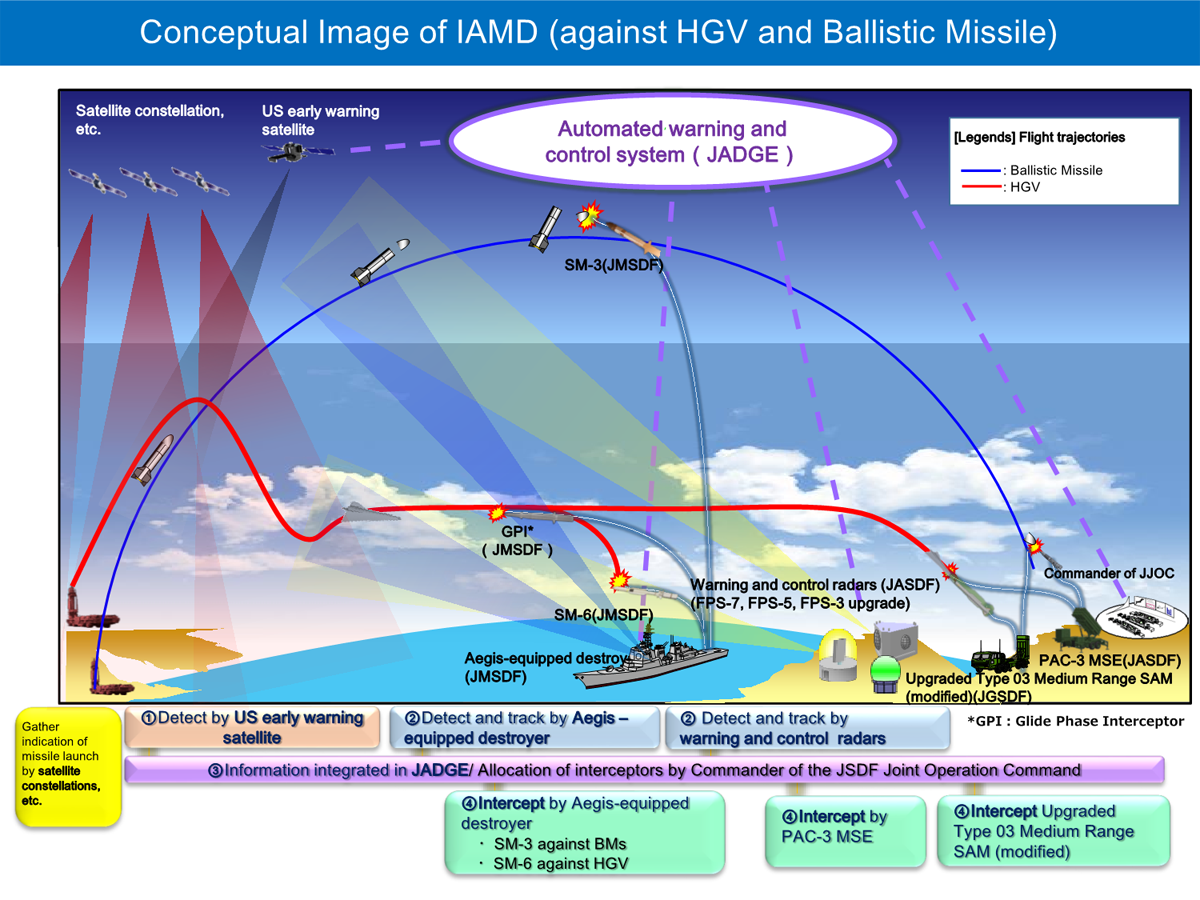
Japan’s ballistic missile defense (BMD) is basically supported by an effective multi-layered defense system composed of the upper tier interception by Aegis-equipped destroyers and the lower tier interception by Patriot Advanced Capability-3 (PAC-3), both of which are interconnected and coordinated by the Japan Aerospace Defense Ground Environment (JADGE).
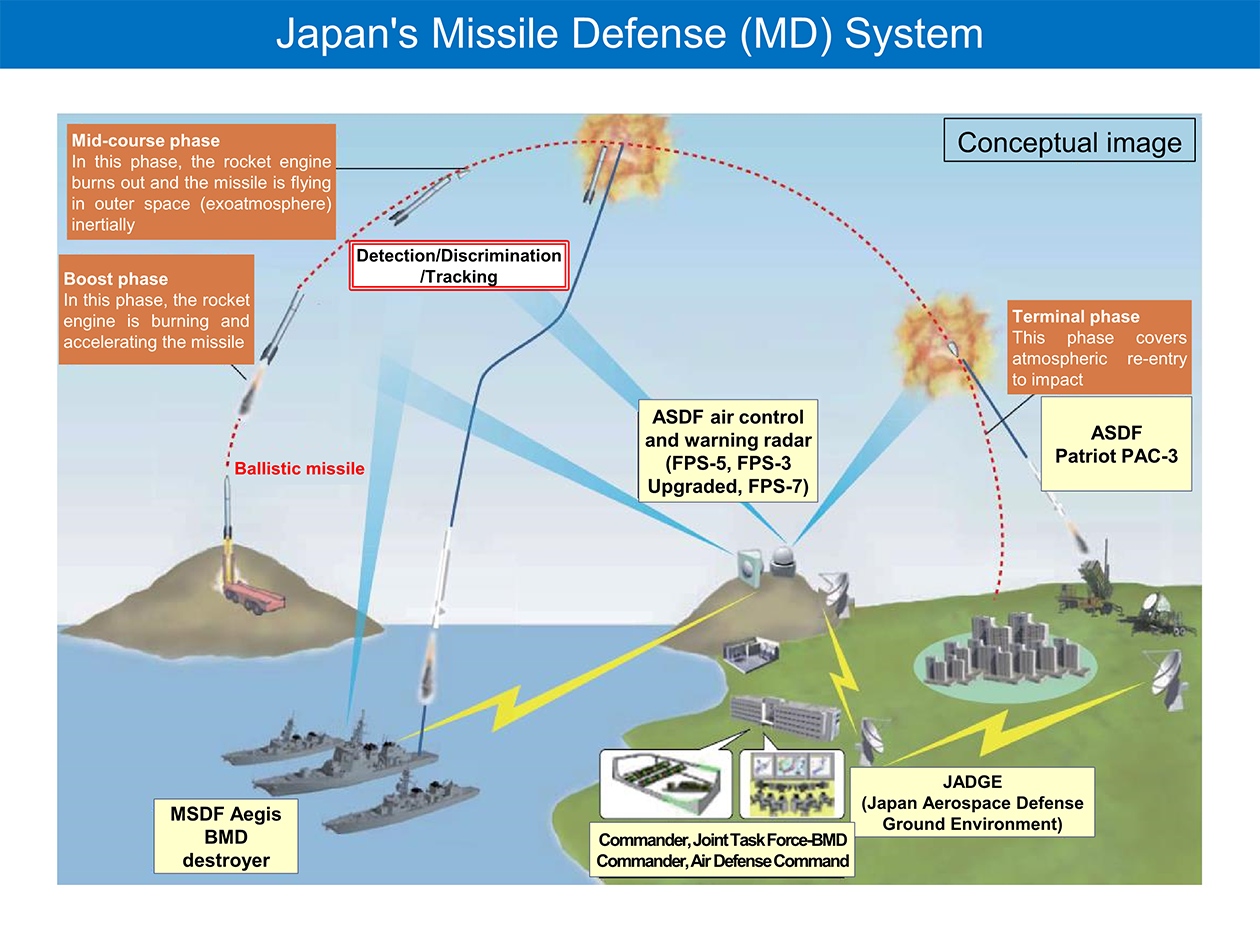
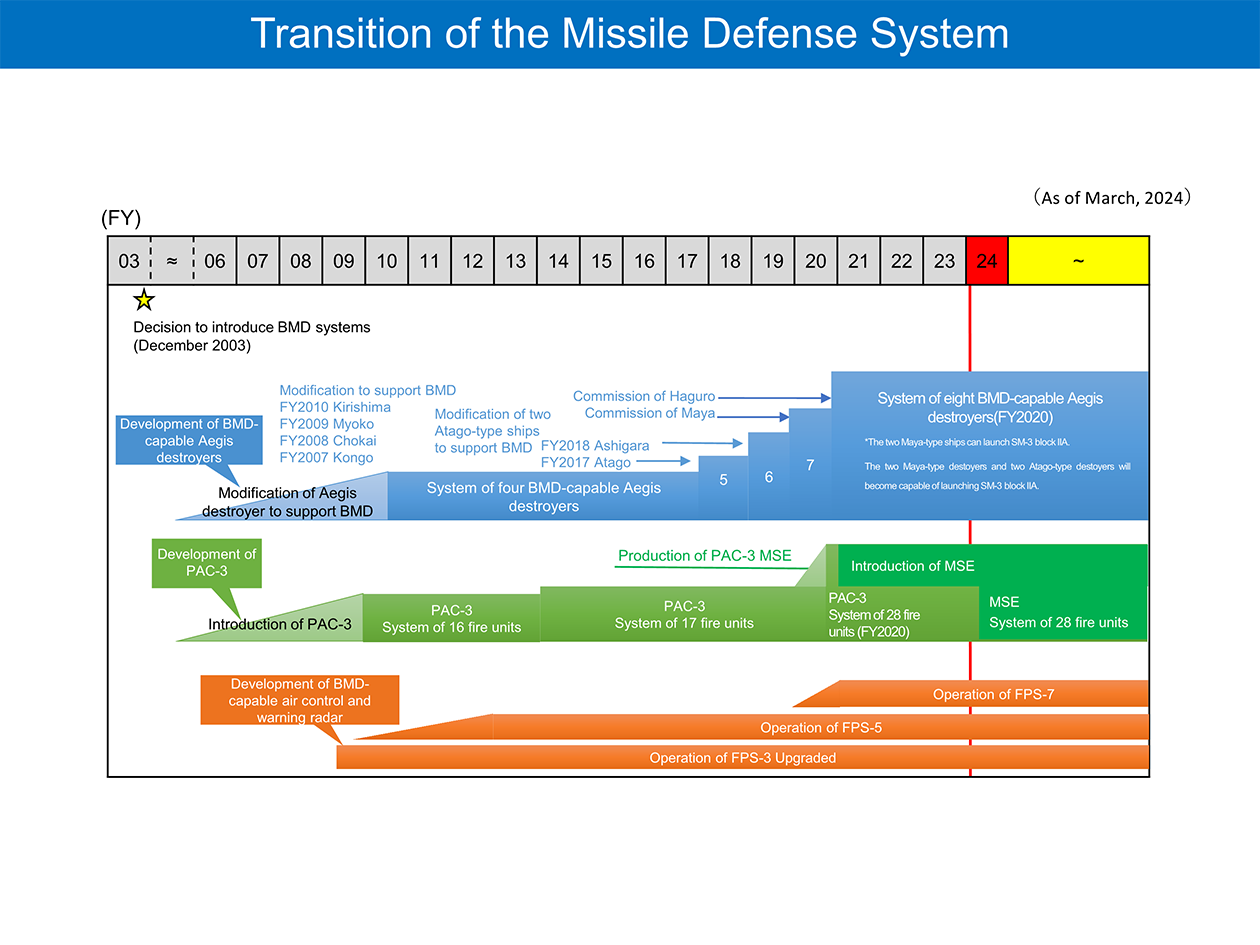
Japan has begun developing its Missile Defense (MD) system since JFY2004 to be fully prepared for the response against ballistic missile attacks.
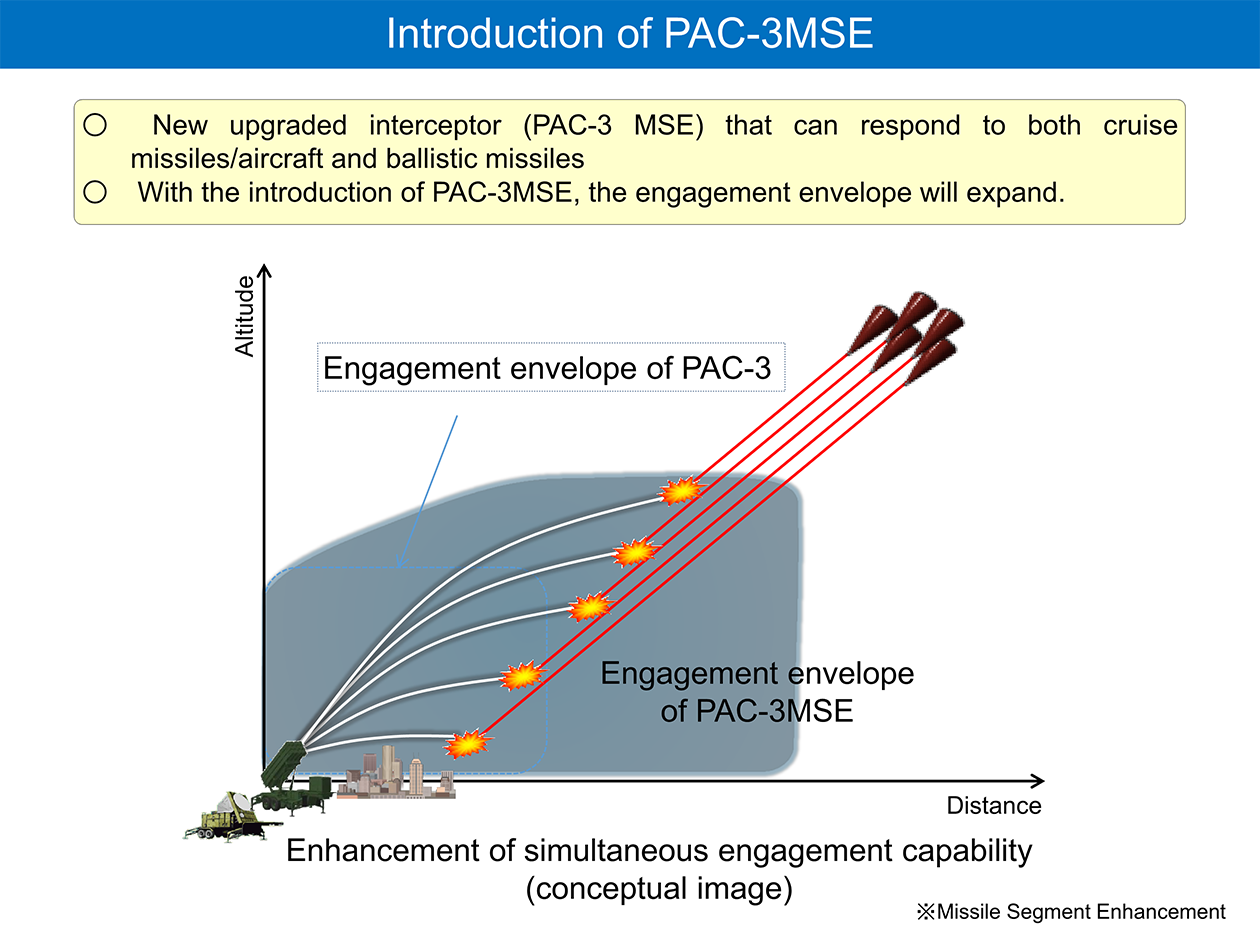
Japan has steadily built up its own defense system against ballistic missile attacks, by such means as installing ballistic missile defense capability in the Aegis destroyers and deploying PAC-3.
For a response to ballistic missiles, the Self Defense Forces (SDF) maintains multi-layered air defense system with 8 Aegis equipped destroyers and PAC-3 units across the country. SDF also maneuvers and deploys those vessels and units that are allocated for stationed-sites’ air defense to respond to the situation.
When destruction measures against ballistic missiles, etc. are ordered, the Joint Task Force (JTF) -BMD will be organized with the Commander of the Air Defense Command serving as the JTF Commander, and effective defense measures will be taken under a unified command through JADGE.



Emerging Threats
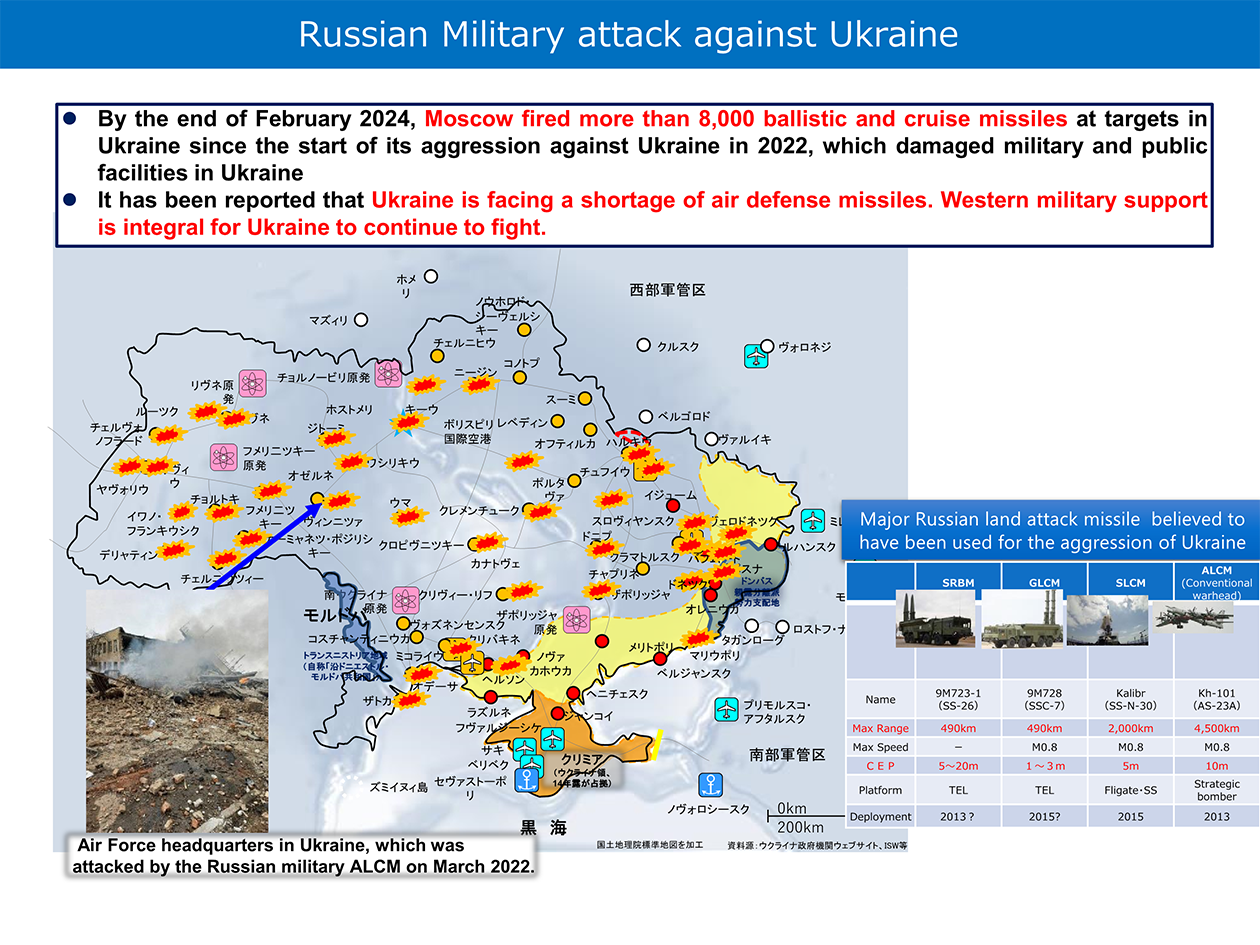
In recent years, missile forces in the area surrounding Japan have been significantly improved both in quality and in quantity, and missile launches have been repeated, making missile attacks against Japan a palpable threat.
Neighboring countries, etc. have improved their launch secrecy and instantaneity by launching missiles from a variety of platforms, such as the Transporter Erector Launcher (TEL) and submarines, and have also improved their precision strike capabilities.
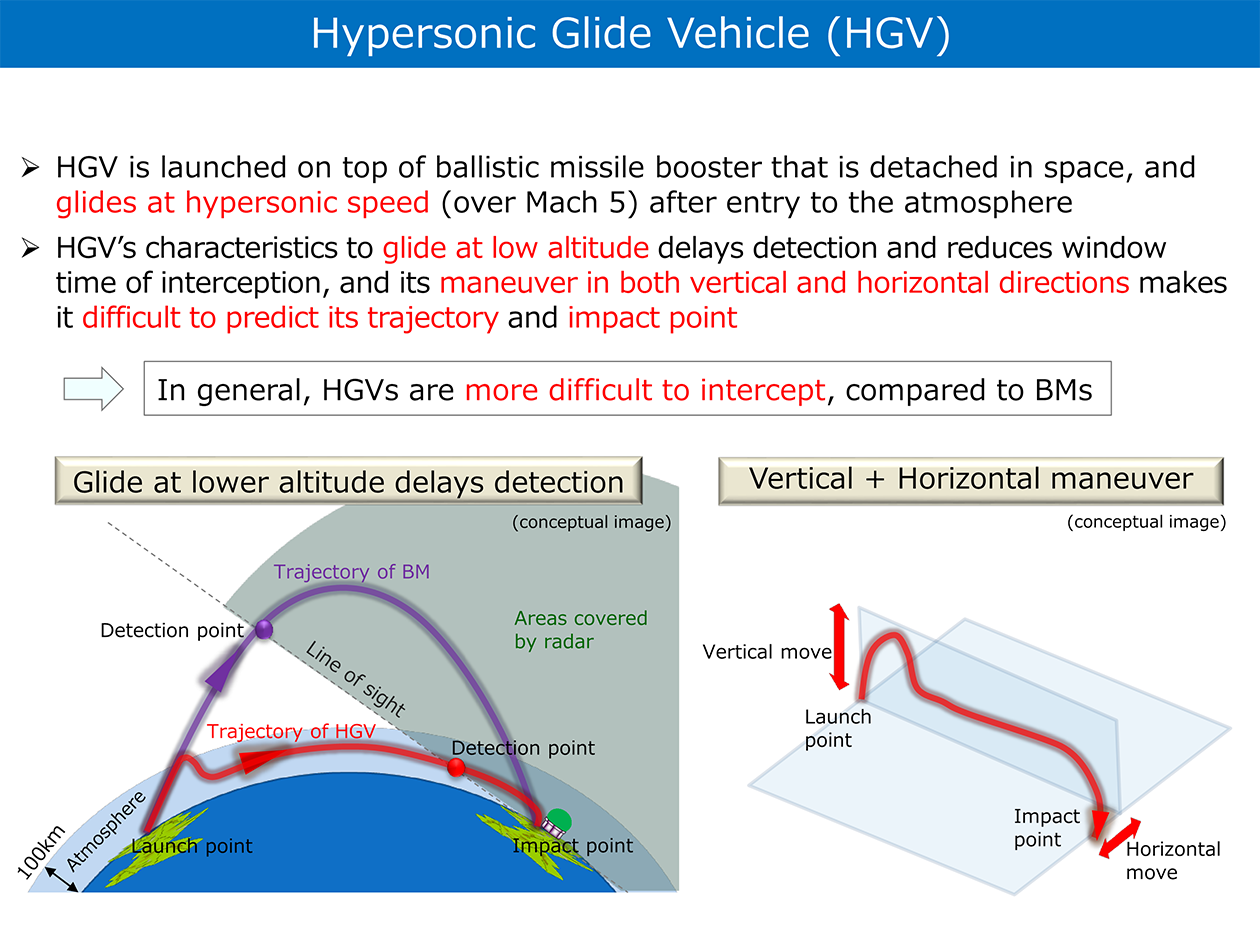
In addition, they are also developing and deploying hypersonic weapons, including Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs), which are said to glide and maneuver at hypersonic speeds (Mach 5 or above) in inner space to hit their targets, and Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs), which use scramjet engines and other technologies that enable hypersonic flight, as well as ballistic missiles that fly on irregular trajectories at low altitudes.



Reference URL
North Korea’s WMD and Missiles (Defense of Japan 2023 p.104-120)
China’s Nuclear and Missile Forces (Defense of Japan 2023 p.60-63)
China’s Air Forces and Naval Forces (Defense of Japan 2023 p.63-67)
Russia’s Nuclear and Missile Forces/New Types of Weapons (Defense of Japan 2023 p.130-133)
Integrated Air and Missile Defense
In recent years, along with the improvement of the capabilities of ballistic missiles, the emergence of hypersonic weapons has diversified, complicated, and advanced the airborne threat.
To this end, Japan will fundamentally reinforce detecting, tracking and intercepting capabilities, and also establish a system to enable unified and optimized operation of various sensors and shooters through networks to reinforce integrated air and missile defense capabilities.
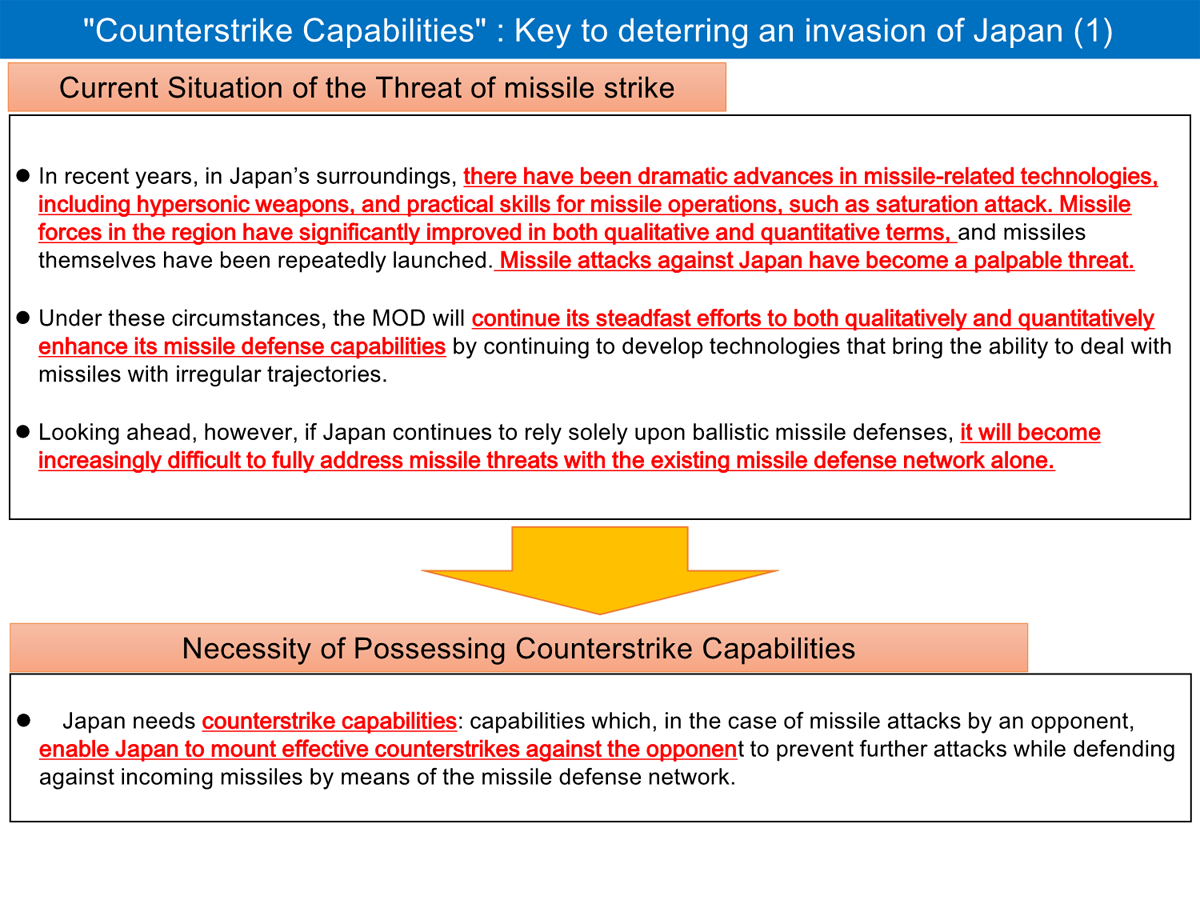
On the other hand, in the area surrounding Japan, there have been significant advances in missile-related technologies, including hypersonic weapons, and practical skills for missile operations, such as saturation attack. Looking ahead, if Japan continues to rely solely upon ballistic missile defenses, it will become increasingly difficult to fully address missile threats with the existing missile defense network alone.
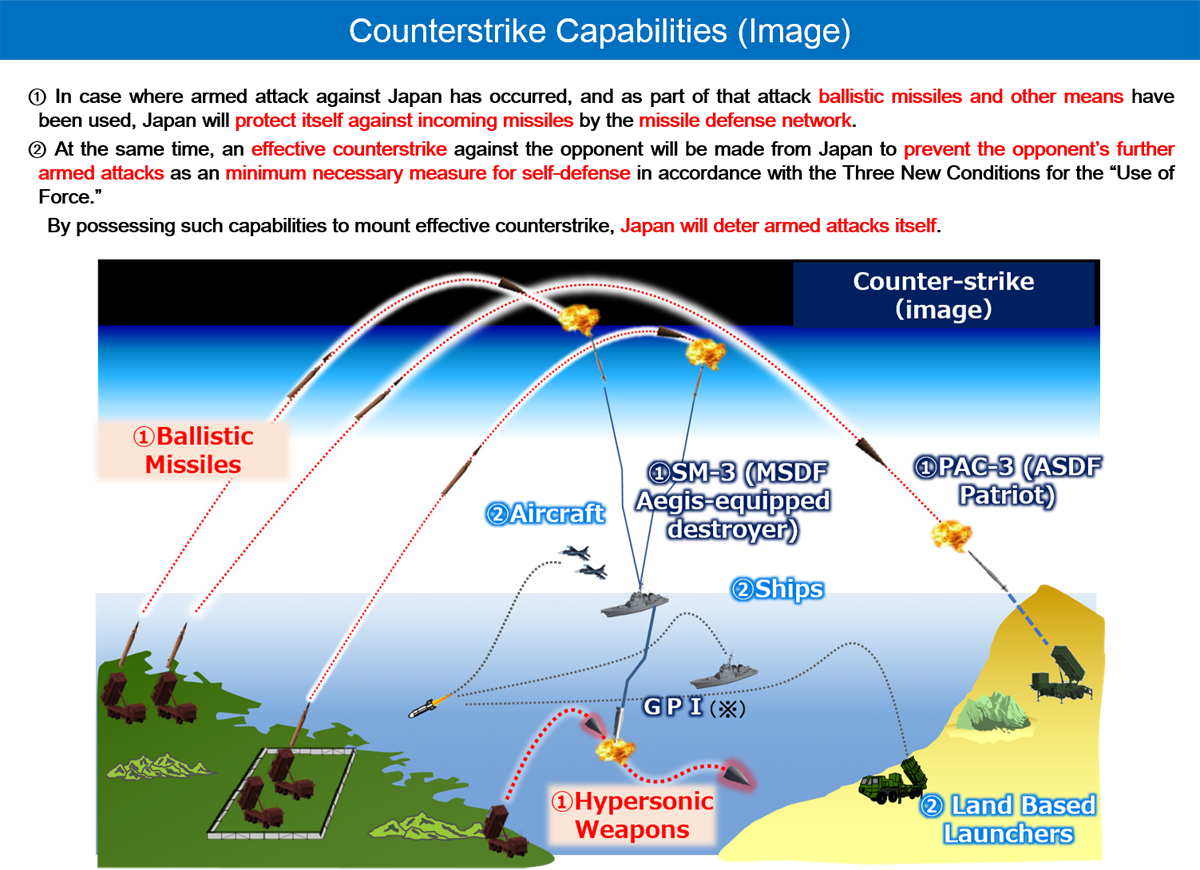
To this end, National Defense Strategy, etc. define that Japan will acquire counterstrike capabilities to enable Japan to mount effective counterstrikes against the opponent’s territory. Counterstrikes are done as a minimum necessary measure for self-defense.
The documents define “Integrated Air and Missile Defense” as follows; Japan will intercept missile attacks using its missile defense network which will have been reinforced both in quality and in quantity in the years to come. Also, by having counterstrike capabilities, Japan will restrict opponent’s missile launches and thereby deter missile attacks from happening.
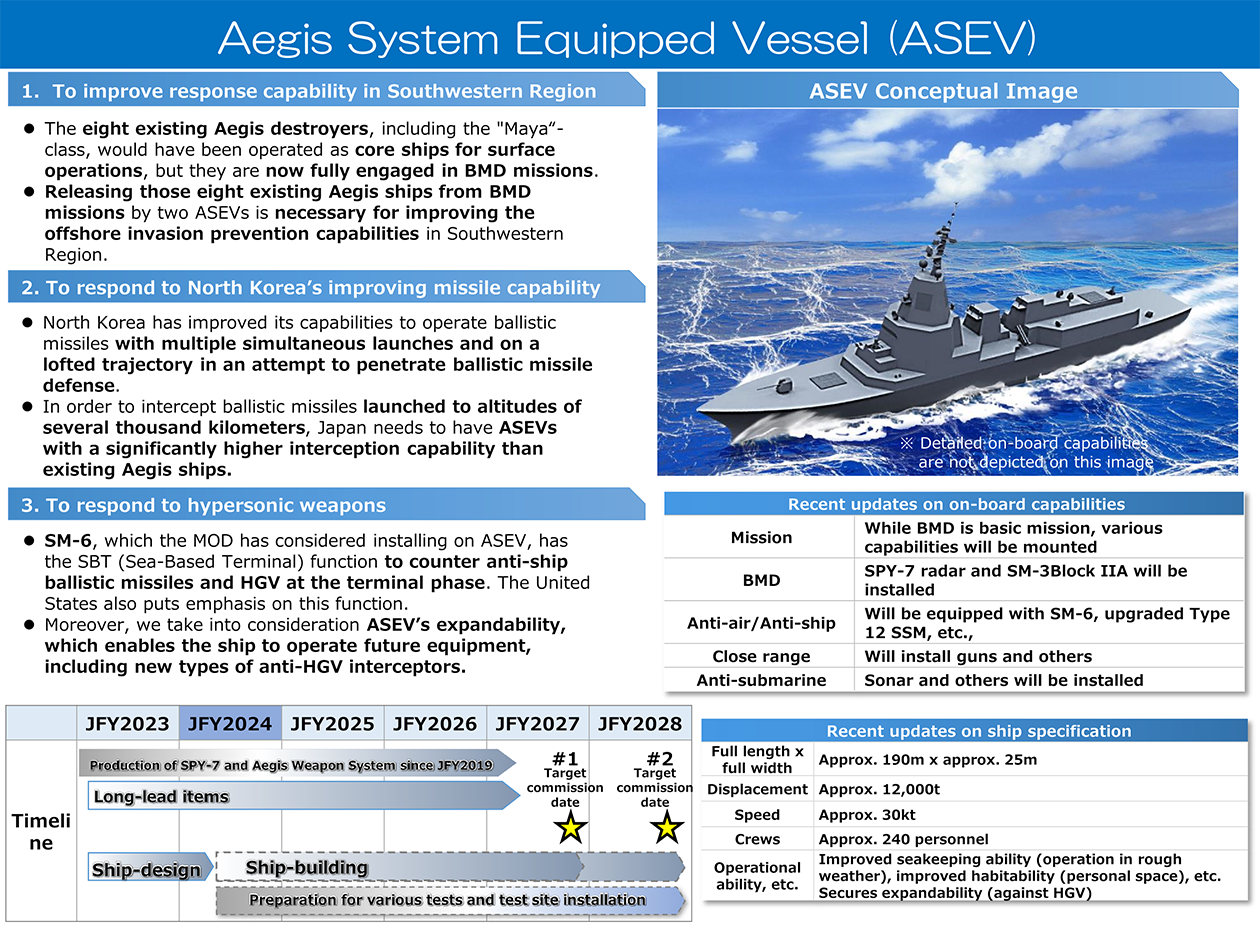
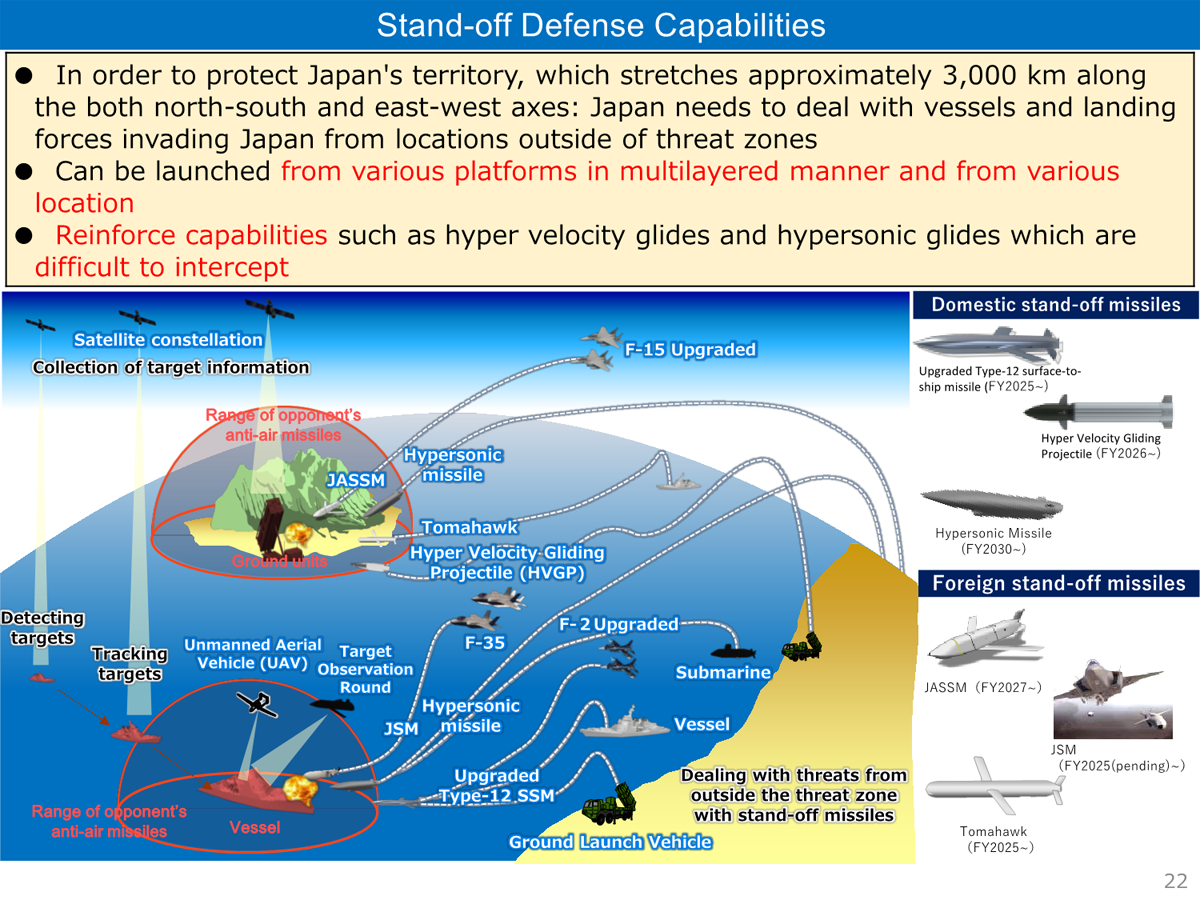
In addition, the Ministry of Defense/SDF will fundamentally reinforce its stand-off defense capabilities that are to be used as a counterstrike capability, to deal with vessels and landing forces invading Japan, including its remote islands, from locations outside of threat zones.




Reference URL
Responses to Missile Attacks (Defense of Japan 2023 p.314-321)